Headline News Archive
 Grants up to $4,000 available to Oak Ridge Associated Universities (ORAU) Consortium member universities
Grants up to $4,000 available to Oak Ridge Associated Universities (ORAU) Consortium member universities
ORAU’s FY 2023 Innovation Partnerships Program (formerly Events Sponsorship Grant Program) is being restructured to build stronger relationships between university members and ORAU subject matter experts. These updates are designed to focus on research and education topics that align well with ORAU’s expertise and current priorities.
Applications must be focused on one or more of the FY 2023 ORAU core focus areas.
An ORAU subject matter expert will serve as a collaborator with the university PI.
The goal of this grant program change is to drive new opportunities for university consortium members and ORAU experts to formulate meaningful collaborations.
Innovation Partnerships grant applications are currently being accepted and the application window will remain open throughout the fiscal year depending on available funds.
Each member university is limited to one award per fiscal year. Up to $4,000 may be requested to support an in-person or virtual event that involves participants from more than one ORAU member institution, including students. Innovation Partnership applications should focus on focused workshops/conferences that highlight your university’s strategic STEM research and education growth areas, and where collaborations with other member universities would add value. We are specifically interested in events that can bring more thought leadership in building a national strategy for STEM education and workforce development. Member universities are encouraged to collaborate around this topic in anticipation of federal funding initiatives.

Join the first interdisciplinary graduate program in the nation, Master of Science in Climate and Health (U-MSCH), at UM. This program trains future generations of clinicians, professionals, researchers, meteorologists, planners, decision-makers and leaders to address the 21st century challenges of the health effects of climate, climate change, weather patterns and weather anomalies (C2W2). The program will provide critical interdisciplinary training needed to:
- understand and investigate an intricate relationship between health and climate, and
- tease out present and future disease and disability burden of C2W2 and its management
Now, we are accepting applications for our Master of Science in Climate and Health Program for the fall of 2023 at the University of Miami.
Mission: Provide students with the state-of-the-art interdisciplinary training in understanding, characterizing and managing the health effects of climate, climate change, weather and weather anomalies (C2W2).
Duration: Two-year Master’s Degree
Tracks:
- Toxicology (pre-med)
- Public Health Sciences
- Marine and Atmospheric Sciences
- Climate and Health - Analytical
Opportunities to pursue research with interdisciplinary faculty members from five colleges
Limited research assistantships may be available
Program details and application information available on the UM Climate & Health website
The U.S. Global Change Research Program is expected to release the first-ever U.S. National Nature Assessment in 2026.
The National Nature Assessment will draw on expertise from the Federal Government, Indigenous communities, academia, non-profit organizations, and the private sector. The Assessment team will hold an array of public engagement opportunities to ensure the report answers questions that are important to every American’s life, and is informed by the best available evidence. Public comments are open through March 31, 2023.

“Fjords punch far above their weight in their ability to pull out a lot of carbon from the atmosphere and store it in the mud,” said Brad Rosenheim, geological oceanography professor and paleoclimate expert at the USF College of Marine Science, who explained that scientists only learned of this small-but-mighty role recently. In 2015, an ocean geochemist and professor at the University of Florida, Thomas Bianchi, pioneered a Nature Geosciences study, with his graduate student at the time, Richard Smith (now at Global Aquatic Research LLC), that first opened scientists’ eyes to the powerful role that fjords play in global carbon storage, he said.
Full article available on USF's College of Marine Science website
 The RCAP 3.0 was developed with the guidance of more than 150 subject matter experts as well as with the input of community members and stakeholders. It outlines goals, recommendations and supporting strategies across 11 focal areas to advance the objectives of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 compared to a 2005 baseline, and of strengthening the adaptive capacity and climate resilience of the region's communities, institutions and economy.
The RCAP 3.0 was developed with the guidance of more than 150 subject matter experts as well as with the input of community members and stakeholders. It outlines goals, recommendations and supporting strategies across 11 focal areas to advance the objectives of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 compared to a 2005 baseline, and of strengthening the adaptive capacity and climate resilience of the region's communities, institutions and economy.
First developed in 2012, the RCAP is a voluntary framework designed to align, guide and support the acceleration of local and regional climate action in Southeast Florida to realize a healthy, prosperous, more equitable and resilient, low-carbon region.

Florida State University has launched a new program to jumpstart research opportunities addressing sustainability and climate change issues.
The program will award grants of up to $150,000, with a total of $1 million available in the 2022-2023 academic year. Interdisciplinary and collaborative proposals are strongly encouraged. The goal is to act as a catalyst for further work on these topics. With that in mind, recipients are expected to pursue external grant funding at the conclusion of their projects.
Research proposals can focus on any aspect of sustainability, including the environmental, social, and economic dimensions of sustainability. They can also deal with issues around climate change, such as mitigation, risk assessment and management, adaptation, resilience and more.
Read the news piece on FSU's University News website.
Visit the program website for more information. Proposal submissions from faculty will be accepted through Feb. 9, 2023. Award decisions will be made in April 2023.
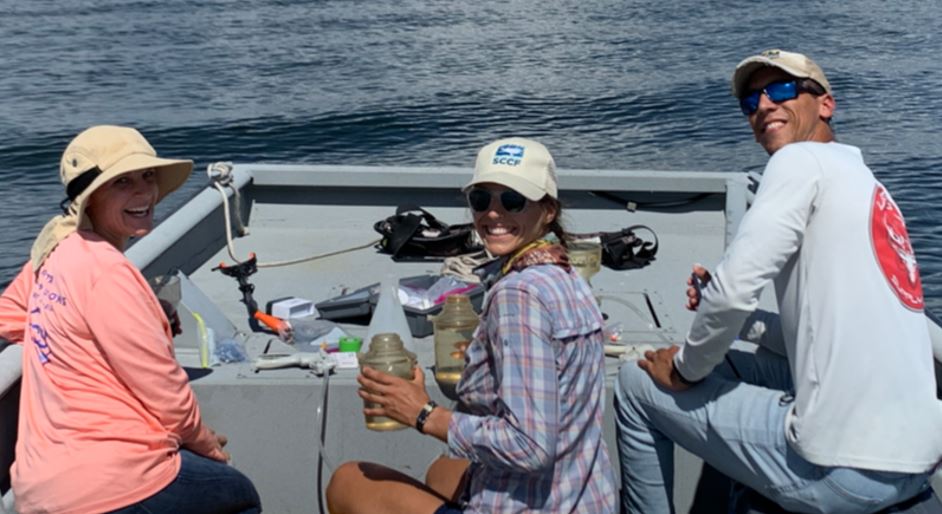
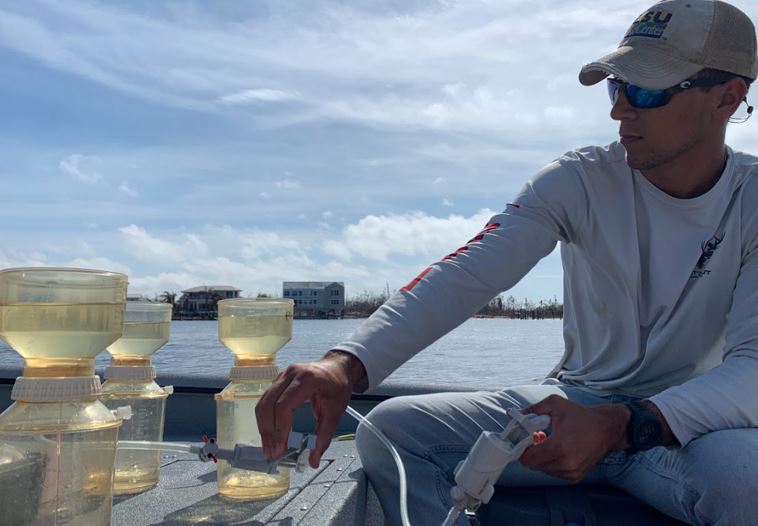 Hurricane Ian left behind a staggering trail of damage to communities and the environment in southwest Florida. A steady stream of response and recovery efforts, from emergency rescues to rebuilding of critical infrastructure, has been underway since the storm brought record breaking winds and rainfall. Alongside these efforts, the UF Center for Coastal Solutions has embarked upon a collaborative effort to understand how the hurricane affected water quality and ecosystems in the region.
Hurricane Ian left behind a staggering trail of damage to communities and the environment in southwest Florida. A steady stream of response and recovery efforts, from emergency rescues to rebuilding of critical infrastructure, has been underway since the storm brought record breaking winds and rainfall. Alongside these efforts, the UF Center for Coastal Solutions has embarked upon a collaborative effort to understand how the hurricane affected water quality and ecosystems in the region.
Quickly after landfall, the CCS and partners Captains for Clean Water, Coastal and Heartland National Estuary Partnership (CHNEP), Charlotte County, South Florida Water Management District (SWFWMD), Sarasota Bay Estuary, and Sanibel-Captiva Conservation Foundation (SCCF) mobilized to sample coastal waters for harmful algae, nutrients, oxygen, and fecal indicator bacteria.
These data are important for estimating the amount and types of pollutants that entered the estuary during the storm and understanding their impacts on human and ecological health. Beyond directly sampling and analyzing water quality, the CCS launched a post-Ian water quality working group involving over 15 organizations including local, state, and national agencies, and environmental organizations.
This valuable work to assess water safety is funded in part by the US Army Corps of Engineers and will continue until April 2023.
The water sampling team working off of Sanibel Island, left to right: UF CCS Director, Christine Angelini, Ph.D.,
SCCF Water Quality Technician Sierra Greene, and CCS Field Technician Adam Hymel

By Thomas Ruppert
Florida’s coastal communities face unprecedented challenges with sea-level rise (SLR) as it permanently inundates areas and exacerbates typical coastal hazards. SLR creates novel legal and financial challenges as it impacts infrastructure for which local governments have legal and financial responsibilities. These challenges call for equally novel planning and policy development; such novel thinking, legal research, and drafting often exceed the capacities of small- and medium-sized local governments that frequently lack the staff bandwidth and specialization to independently conduct such work.
Florida Sea Grant (FSG) has, since 2012, been collaborating with the East Central Florida Regional Planning Council (ECFRPC) to provide legal and policy research, conduct trainings and outreach, and draft legal language for small- and medium-sized communities on Florida’s east central coast. The novel approaches developed by FSG have led the way for small- and medium-sized local governments in the region through approaches and planning policies that focus on grounding today’s policy and actions in long-term visions balancing desires for coastal protection and infrastructure services with the fiscal and physical realities of our changing coast. Areas of focus include comprehensive plan language seeking to minimize potentially crippling legal and fiscal liabilities for infrastructure and shifting the focus of infrastructure services from reactive to specific property owner complaints to proactive based on current and future scenarios focused on infrastructure services as part of a system serving communities of people. As part of the ECFRPC’s Regional Resiliency Collaborative and co-developer of the ECFRPC-led “Regional Resilience Action Plan,” FSG has been instrumental in developing policies and working with the ECFRPC to disseminate them.
FSG and Thomas Ruppert served as a driving force in the City of Satellite Beach’s adoption of Adaptation Action Areas language in their comprehensive plan—the first municipality in Florida to do so. In Ordinance 1160, Satellite Beach became the first municipality we are aware of in Florida to explicitly state in its land development code that its policies seek “to promote a managed retreat from the sensitive ocean bluff and Erosion Adaptation Action Areas.”[1] This represents a shift away from hard armoring of our coastlines and recognition of a changing future. Satellite Beach approved Ordinance 1194 on March 17, 2021. This ordinance adopted virtually verbatim extensive FSG comprehensive plan recommendations. Ordinance 1194 modified Satellite Beach’s Comprehensive Plan elements for Infrastructure, Coastal Management, Intergovernmental Coordination, Capital Improvements, and Future Land Use. As of January 2022, at least nine additional local governments in the ECFRPC’s region have adopted language drafted by FSG, edited by FSG, or drafted by the ECFRPC with input from FSG, including: Brevard County, Cape Canaveral, Cocoa, Melbourne Beach, New Smyrna Beach, Oak Hill, Rockledge, Titusville, and Volusia County. As part of the ECFRPC’s “Regional Resilience Collaborative,” more local governments in the area are expected to likely adopt language based on the resilience work of FSG and ECFRPC. In September of 2022, Satellite Beach adopted an ordinance and supporting documents created by FSG to integrate additional recommendations on notice of sea-level rise to permit applicants. FSG continues to collaborate with Satellite Beach and partners to move forward resilience in Satellite Beach and the many communities emulating Satellite Beach’s approach.
Florida Sea Grant is leading the way in developing holistic legal and planning examples for small- to medium-sized local governments attempting to balance local government fiscal constraints and the realities of sea-level rise through adaptations grounded in long-term visions informing short-, medium-, and long-term actions designed to maximize the quality of life, economic outlook, and safety of coastal governments on our changing coastline. Local governments are responding by adopting FSG-drafted/inspired language into their comprehensive planning for resilience and into ordinances.
 On Day One of the Forum, FEMA’s Acting Deputy Administrator for Resilience Victoria Salinas said that the RNPN represents the “whole community” because of the diverse array of invested community leaders from across the nation. Throughout the Forum, thousands of people joined the conversations, underscoring keen interest to further resilience.
On Day One of the Forum, FEMA’s Acting Deputy Administrator for Resilience Victoria Salinas said that the RNPN represents the “whole community” because of the diverse array of invested community leaders from across the nation. Throughout the Forum, thousands of people joined the conversations, underscoring keen interest to further resilience.
In case you missed any of the Forum presentations, here are videos from each day:
Day 1 – Social Cohesion: Making Access, Inclusion, and Equity Priorities in Resilience
Day 2 – Making Resilience Priorities Complementary
Day 3 – Inclusive Design: Building a Sense of Resilient Belonging
Day 4 – Voices of Inclusive Resilience
Wednesday, January 25, 2023 will be the formal kickoff of the Stories of Resilience initiative. Please save the date to learn more about Stories of Resilience and why storytelling is a critical tool for building community resilience.
 Three Florida Climate Institute partners will participate in the spring 2023 studio to reimagine NCF. Modeled after two multi-university, multi-disciplinary challenges in the Northeast, Envision Resilience, which studied Nantucket, MA and Narragansett Bay, RI, the New College Challenge aims to build partnerships with students, leaders from major statewide and national universities, and experts across key industries. These thought leaders will address the social, economic and environmental challenges that face New College and present a hopeful vision for the future.
Three Florida Climate Institute partners will participate in the spring 2023 studio to reimagine NCF. Modeled after two multi-university, multi-disciplinary challenges in the Northeast, Envision Resilience, which studied Nantucket, MA and Narragansett Bay, RI, the New College Challenge aims to build partnerships with students, leaders from major statewide and national universities, and experts across key industries. These thought leaders will address the social, economic and environmental challenges that face New College and present a hopeful vision for the future.
More info at https://www.ncf.edu/Challenge/
 University of Florida students are invited to participate in the 2nd Annual Campus Climate Corps Conference. The conference is in two parts, a 4-hour live, virtual event on Friday, November 4 from noon to 4pm and a series of hour-long daily briefings from the UN climate conference (COP27) from Nov 5 to Nov 18 in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt.
University of Florida students are invited to participate in the 2nd Annual Campus Climate Corps Conference. The conference is in two parts, a 4-hour live, virtual event on Friday, November 4 from noon to 4pm and a series of hour-long daily briefings from the UN climate conference (COP27) from Nov 5 to Nov 18 in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt.
Details available on Campus Climate Corps website
 Stetson University’s Institute for Water and Environmental Resilience (IWER) received a Stage 1 Civic Innovation Challenge (CIVIC) planning grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) for a project designed to help the City of Cape Canaveral reduce flooding and improve water quality in the face of rising seas. Jason Evans, PhD, IWER’s executive director and associate professor of Environmental Science, is the principal investigator for the project.
Stetson University’s Institute for Water and Environmental Resilience (IWER) received a Stage 1 Civic Innovation Challenge (CIVIC) planning grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) for a project designed to help the City of Cape Canaveral reduce flooding and improve water quality in the face of rising seas. Jason Evans, PhD, IWER’s executive director and associate professor of Environmental Science, is the principal investigator for the project.
The overall goal of the project is for the partners to work with Cape Canaveral to implement and carefully measure the performance of nature-based infrastructure – such as rain gardens, constructed wetlands and permeable pavement – in areas with known flooding concerns.
Undergraduate students and community volunteers will assist researchers with the collection and interpretation of field data, providing a regional model for partnership and innovation in climate adaptation.
The CIVIC project builds upon several years of ongoing collaboration between IWER, the East Central Florida Regional Planning Council and Florida Sea Grant to characterize and quantify Cape Canaveral’s substantial flooding challenges. For example, IWER currently maintains a network of three advanced water-level sensors in Cape Canaveral, which together captured critical hydrologic data during several recent flooding events, including Hurricane Ian.
IWER is one of 56 teams across the country to receive a $50,000 Stage 1 planning grant through CIVIC, which is funded by NSF in partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy and U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Read the full article in Stetson Today.
Dr. Savanna Barry led a team from UF to develop the proposal “Engaging Communities to Design Nature-based Solutions to Mitigate Climate-related Hazards” to the Gulf Research Program. The grant received funding to build on long-term Florida Sea Grant and IFAS Extension engagement with the City of Cedar Key on climate and coastal issues.
This project focuses on the importance of nature-based solutions as part of Cedar Key’s strategy to mitigate climate-related hazards. The project will work with citizens of Cedar Key to understand their preferences for mitigating the impact of erosion and rising seas on a critical road and park area in Cedar Key even as the project also seeks to improve water quality and stormwater flooding problems. This is an initial proposal to develop a conceptual design proposal. If the conceptual design is well received, the second phase is an application for funding to develop detailed engineering design. Other team members from UF include Dr. Michael Allen, Dr. Mark Clark, Dr. Jason von Meding, Dr. Xiao Yu, and Thomas Ruppert, Esq.
 The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine set to release Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information for Decision Making.
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine set to release Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information for Decision Making.
Climate change, driven by increases in human-produced greenhouse gases and particles (collectively referred to as GHGs), is the most serious environmental issue facing society. The need to reduce GHGs has become urgent as heat waves, heavy rain events, and other impacts of climate change have become more frequent and severe. Since the Paris Agreement was adopted in 2015, more than 136 countries, accounting for about 80% of total global GHG emissions, have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. A growing number of cities, regional governments, and industries have also made pledges to reduce emissions. Providing decision makers with useful, accurate, and trusted GHG emissions information is a crucial part of this effort.
The full description and info on how to order available here

A new threat has become apparent: Arctic lakes are drying up, according to research published in the journal Nature Climate Change. The study, led by UF Department of Biology postdoctoral researcher Elizabeth Webb, flashes a new warning light on the global climate dashboard.
Webb’s research reveals that over the past 20 years, Arctic lakes have shrunk or dried completely across the pan-Arctic, a region spanning the northern parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, Scandinavia and Alaska. The findings offer clues about why the mass drying is happening and how the loss can be slowed.
The vanishing lakes act as cornerstones of the Arctic ecosystem. They provide a critical source of fresh water for local Indigenous communities and industries. Threatened and endangered species, including migratory birds and aquatic creatures, also rely on the lake habitats for survival.
Read more about Webb's findings here.

This week-long event with guest speakers was designed to help you understand the impacts our changing climate is having on the Sunshine State. Industry leaders and front-line advocates spoke about the effects climate change is having in your community, and how to become a part of the solution to ensure a sustainable planet for future generations.
Hear Tiffany Troxler (FIU) and Kebreab Ghebremichael (USF) discuss Laying the Groundwork for 'Getting to Neutral' in the State of Florida- Presented by Florida Climate Institute Watch recorded session at:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=byrJD224y0w&list=PLzDGN_mfeF7_chlVE-EV8vLYLgdeSvttm&index=6

Researchers at the Florida Institute of Built Environment Resilience at UF are conducting a study about hurricane protective behaviors at institutions of higher education in Florida. They are looking into how housing conditions and physical characteristics of the built environment influence risk perception and intentions of protective behaviors for students, faculty, and staff, with the aim to improve emergency planning and disaster risk management at colleges and universities in Florida.
They will be conducting a large survey and are interested in three campuses in particular; Florida State University (FSU), University of Florida (UF), Florida International University (FIU). The survey should take around 15 minutes, and participants will have the chance to win one of three $150 visa gift cards. They would greatly value and appreciate support/collaboration from the Florida Climate Institute community of practice. For further information, please contact Amer (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.).
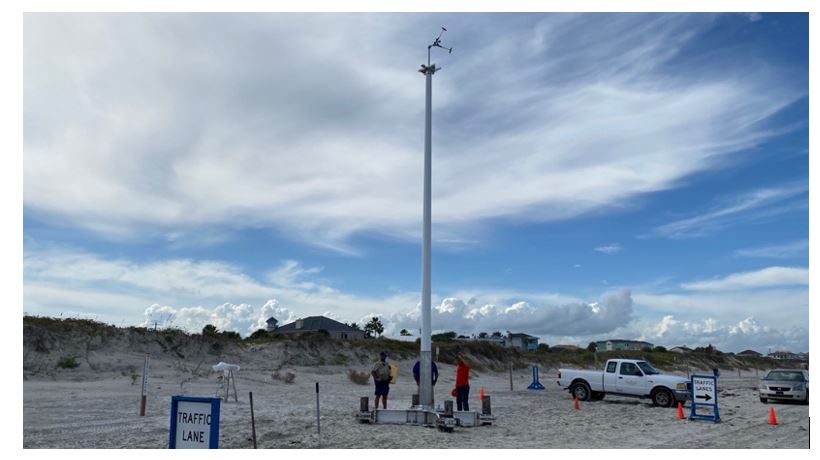 Hurricanes cause widespread interruption to meteorological and hydrological measurement stations exactly at the time when researchers and decision-makers need them most. To fill this observational gap, researchers led by Dr. Forrest Masters (UF) developed a state-of-the-art monitoring station, called a "Sentinel," engineered to operate in and measure extreme wind, storm surge, wave, and hazardous water quality conditions. This platform is currently being used to collect data in the Tampa area by this research group.
Hurricanes cause widespread interruption to meteorological and hydrological measurement stations exactly at the time when researchers and decision-makers need them most. To fill this observational gap, researchers led by Dr. Forrest Masters (UF) developed a state-of-the-art monitoring station, called a "Sentinel," engineered to operate in and measure extreme wind, storm surge, wave, and hazardous water quality conditions. This platform is currently being used to collect data in the Tampa area by this research group.
In 2021, a Mark I Sentinel was designed and prototyped. In contrast to permanent stations that are elevated and hardened to avoid/ resist flooding and waves, the station was designed for temporary installation at the shoreline between the mean tidal datum and the sand dunes. Its system was designed to resist 5 m breaking waves in a 5 m still water depth, accounting for 1 m of combined erosion and pile scour. Data such as 3D wind velocity, pressure, temperature, humidity data, and videos are collected at the top of the mast.
This year, the team, including Dr. Brian Phillips (UF), Dr. Forrest Masters (UF), Dr. Britt Raubenheimer (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute), Dr. Maitane Olabarrieta (UF), Dr. Elise Morrison (UF), Dr. Chris Ferraro (UF), and Dr. Justin Davis (UF), received an NSF Major Research Instrumentation award to support the design of a Mark II Sentinel system and the commissioning of a fleet of six Mark II Sentinels.
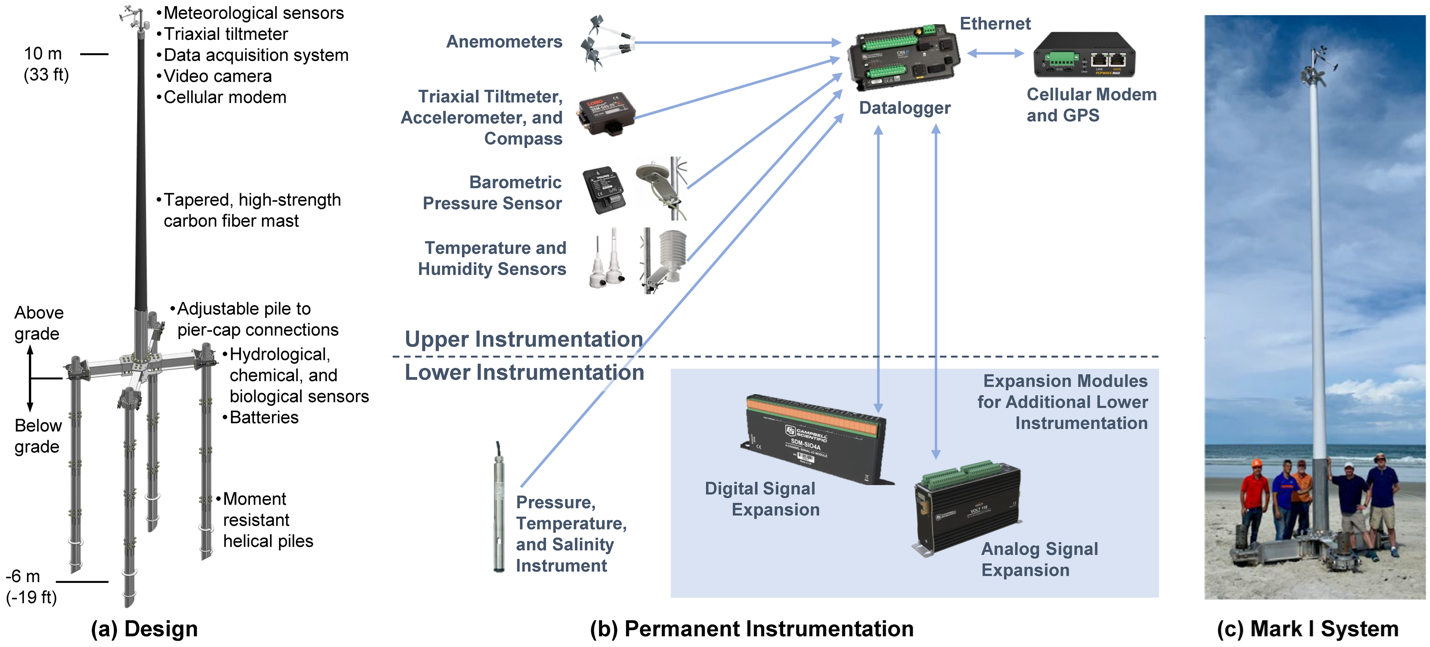
Data and video will be shared with a broad spectrum of research, operational, and commercial partners as well as interests supporting local response and recovery, such as state departments of environmental protection or natural resources. These stations will support fundamental research that includes, but is not limited to, numerical weather prediction, storm surge, shallow wave modeling, boundary layer meteorology, air-sea interaction, biogeochemistry, aircraft- and satellite-based remote sensing of the surface wind and wave fields, and hydrodynamic loading of coastal structures. We wish the team smooth, safe conditions for their deployment this week!

Senator Sheldon Whitehouse was impressed by UF students from Architecture, Historic Preservation, and Journalism who participated in a 6-university challenge to reimagine Narragansett Bay coastal communities during this past semester. All teams traveled to the sites, interacted with local residents and experts, participated in a 10-week lecture series, and created inspiring visions for the future of the Bay.
Professor Jeff Carney led his second group of Architecture students in the Envision Resilience Challenge this year after a huge success in Nantucket last year. Linda Stevenson led the Historic Preservation students and Cynthia Barnett the Journalism students.
This program, coordinated by Carolyn Cox, offers students the chance to work across disciplines, across universities, and within real communities to make an impact while gaining professional experience. This year’s teams hail from UF, Northeastern, Syracuse, Roger Williams, U Rhode Island, and the Rhode Island School of Design (RISD).
Student work will be on exhibit at the Waterfire Arts Center in Providence, RI through June 26.
For more information, see https://www.envisionresilience.org/.














